Power Sharing Class 10 Notes, In a democratic setup, the principle of Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview ensures that no single branch of government holds absolute authority. This chapter delves into the nuanced concept of Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview, drawing insightful examples from Belgium and Sri Lanka, highlighting how democracies manage diverse societal demands for governance.
Belgium: Embracing Diversity in Governance
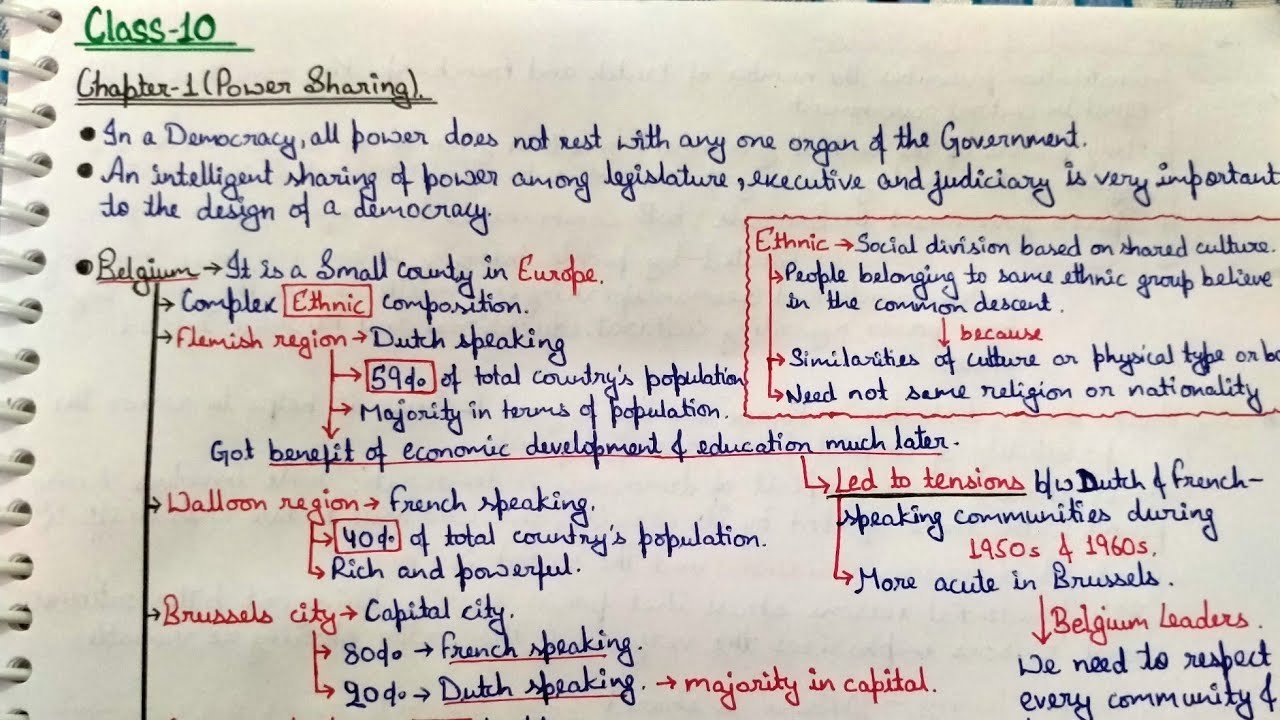
Belgium, a European nation with over 10 million inhabitants, exemplifies cultural diversity and linguistic plurality. It shares borders with France, Germany, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands, fostering a rich tapestry of traditions and languages. The linguistic divide is stark, with Dutch predominant among the majority and French concentrated in Brussels, the capital.
Sri Lanka: Challenges Amidst Cultural Plurality
Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview, an island nation with a population exceeding 20 million, exhibits a mosaic of cultures and languages. Sinhala, spoken by the Buddhist majority, contrasts with Tamil, spoken by both Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview and Indian Tamil communities. Historical tensions exacerbated by discriminatory policies, notably the imposition of Sinhala as the sole official language in 1956, triggered conflict and marginalized Tamil interests.
Majoritarianism in Sri Lanka: Striving for Equity
The adoption of majoritarian policies in Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview, favoring Sinhala speakers in governance and education, marginalized Tamil communities, leading to demands for autonomy and eventual conflict.
Belgium’s Path to Accommodation: Institutional Harmony
Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview responded to linguistic tensions through constitutional amendments, ensuring equitable representation of Dutch and French speakers in governance. Brussels, with its unique governance model, operates with community governments, preserving cultural and linguistic autonomy.
Why Opt for Power Sharing?
Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview mitigates conflicts by ensuring diverse societal voices influence governance decisions. It upholds democratic principles, where decisions reflect collective will, fostering stability and inclusivity in governance structures.
Forms of Power Sharing
Horizontal Distribution: Ensures checks and balances among legislative, executive, and judicial branches, preventing monopolization of power and safeguarding against authoritarianism.
Vertical Distribution: Federalism divides power between central and state governments, accommodating regional diversity while maintaining national unity.
Social and Linguistic Groups: Belgium’s community governments exemplify how diverse groups participate in local governance, preserving cultural and linguistic identities within a unified national framework.
Political Parties and Movements: Coalition governments in democracies illustrate how power is shared among ideological groups, negotiating policies that reflect societal interests.

Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview: FAQs
Q1: What is Majoritarianism? Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview asserts that the majority community should dominate decision-making, potentially sidelining minority interests.
Q2: What is Vertical Distribution of Power? Vertical distribution refers to power allocation between different levels of government—central, state, or provincial—ensuring decentralized governance and responsiveness to local needs.
Q3: How does Power Sharing Promote Stability? By incorporating diverse viewpoints, Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview reduces conflict and promotes societal cohesion, resulting in more inclusive and sustainable governance.
Q4: Can Power Sharing Lead to Inefficiency? While power sharing may slow decision-making, it enhances legitimacy and ensures policies reflect broader societal consensus, promoting long-term stability.
Conclusion
Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview is fundamental to democratic governance, preventing tyranny and promoting societal harmony. Belgium and Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview experiences underscore the importance of equitable governance in managing diversity and ensuring inclusive development. In essence, Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview isn’t just a principle—it’s a cornerstone of resilient democracies capable of addressing complex societal challenges.
For more detailed Power Sharing Class 10 Notes: Comprehensive Overview, including question answers and a downloadable PDF, explore further resources on the topic.